Proportional Integral Derivatives (PIDs)

Understanding Proportional Integral Derivatives (PIDs) Controllers: A Key Component in Automation
PID controllers are vital to industrial automation because they guarantee optimal performance and preserve process control. Proportional, integral and derivative are the three main elements that cooperate to control a system’s output, and they are represented by the abbreviation “PIDs.”. This article will examine the foundations of PID controllers, their uses, and the advantages they offer across a range of sectors.
What is a proportional integral derivatives (PIDs) controller?
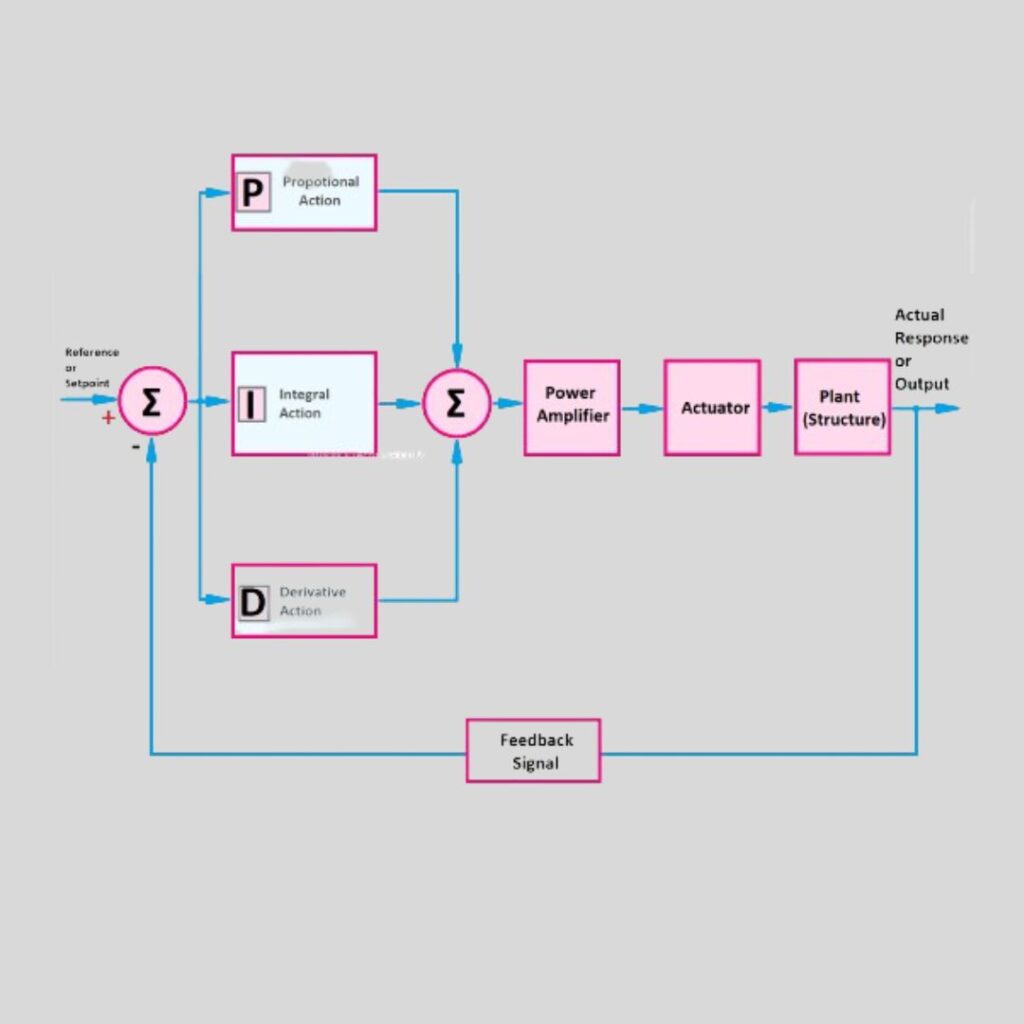
One common control loop feedback technique in industrial control systems is the PID controller. Reaching a desired setpoint by adjusting a process variable such as temperature, pressure, or flow rate is its main purpose. The error is the difference between the planned setpoint and the measured process variable. The controller computes this error continually and uses the proportional, integral, and derivative terms to apply corrective measures.
Proportional Control (P):
An output value proportional to the current error value is generated by a PID controller’s proportional component. Accordingly, the magnitude of the correction required increases with the accuracy. Despite its effectiveness, proportional control frequently leads to a steady-state error, meaning that the process variable is not precisely at the set point.
Integral Control (I):
The steady-state error is addressed by the integral component, which takes the cumulative error over time into account. This part makes adjustments to the controller’s output to remove the residual steady-state error by integrating the error, guaranteeing that the process variable will eventually reach the setpoint. On the other hand, oscillations and overshooting might result from excessive integral motion.
Derivative Control (D):
The derivative component uses the error’s rate of change to forecast future errors. The derivative action serves to reduce overshoot and settling time by dampening the system’s response in response to the rate at which the error is changing. This predictive ability is especially helpful in cases where it is assumed that process conditions will change quickly.
Proportional Integral Derivatives (PIDs) Brand
- Omron
- Schneider
- Siemens
Applications of Proportional Integral Derivatives (PIDs) Controllers
PID controllers are adaptable and have uses in a range of sectors, such as:
Manufacturing:
PID controllers maintain ideal operating conditions for machines by controlling temperature, pressure, and flow rates during production processes. In order to minimise waste and ensure product quality, this management is necessary.
Chemical Processing:
Exact control of reaction conditions is essential in chemical facilities. PID controllers optimise reaction speeds and guarantee safety by assisting in maintaining the correct concentrations of reactants and products.
HVAC Systems:
HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems rely heavily on PID controllers. They maximise energy efficiency and provide comfort by controlling humidity and temperature.
Robotics:
PID controllers in robotics allow automated systems and robotic arms to move and position precisely. Through feedback-driven adjustments to speed and direction, they improve robotic operations’ accuracy.
Benefits of Using PID Controllers
PID controllers have a lot of benefits:
Precision:
PID controllers increase process dependability and product quality by providing great accuracy in maintaining target setpoints.
Stability:
PID controllers can be tuned to minimise oscillations and fluctuations and assure steady operation by adjusting the derivative, integral, and proportional components.
Flexibility:
PID controllers are easily adaptable to meet individual requirements and can be used in a wide range of processes.
Automation:
By reducing the need for manual intervention, PID controller integration into automated systems improves operational efficiency.
