Contactors

Understanding Contactors: Essential Components for Power and Automation
Our goal at Rudra Power & Automation is to give our clients a comprehensive understanding of the electrical components that promote safety and efficiency in industrial settings. The contactor is one such essential part. The definition, kinds, uses, and importance of contactors in power and automation systems will all be covered in this article.
What is a contactor?
An electrically operated switch used to regulate a power circuit is called a contactor. Electric motors, lighting, heating, and other loads are its main uses. Contactors, which are usually utilised in commercial and industrial settings, are made to manage higher currents than relays.
Key Components of a Contactor
- Coil: When activated, the electromagnetic coil produces a magnetic field that closes the connections.
- Contacts: The conductive components that open and close the circuit are called contacts. Depending on the application, contacts might take many forms.
- Arc Chamber: This part is intended to prevent damage to the system by putting out the arc that develops when the contacts open and reopen.
- Frame: The frame offers structural stability and contains the components.
Contactors Brand
- General Electric (GE)
- Rockwell Automation
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens
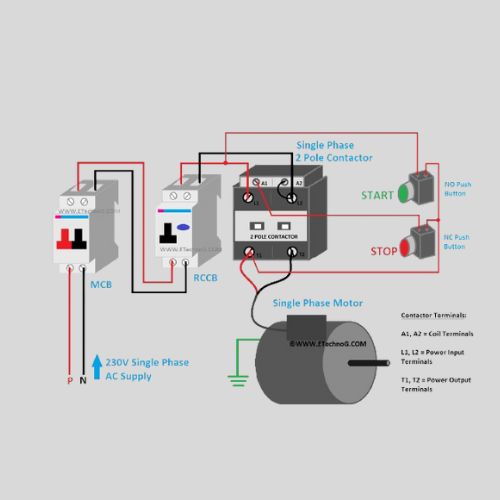
Types of Contactors
There are several varieties of contactors, and each is appropriate for a particular use:
AC Contactors:
Applications involving alternating current (AC) are the focus of AC contactor design. Motors, lighting circuits, and other inductive loads frequently employ them. Because of their ability to manage strong inrush currents, AC contactors are appropriate for use in industrial environments.
DC Contactors:
Direct current (DC) applications are the focus of DC contactor design. Electric cars, battery systems, and other DC-powered devices employ them. Different design considerations are needed for DC contactors in order to handle the particular difficulties presented by direct current.
Smart Contactors:
Due to their communication capabilities, smart contactors can be integrated into automated systems. They are perfect for advanced automation systems and smart grid applications since they can be remotely monitored and controlled.
Reversing Contactors:
A motor’s direction can be altered with the use of these contactors. Reversing contactors enable smooth motor operation in both clockwise and anticlockwise directions by managing two independent contactors.
Applications of Contactors
Contactors are essential in a wide range of applications in numerous industries.
Motor Control:
Motor control is one of the main uses for contactors. They make it possible for motors to start and stop, facilitating effective operation in industrial and manufacturing processes.
Lighting Control:
Lighting systems in commercial buildings are managed by contactors. Facility managers can increase energy efficiency by automating lights based on occupancy or time by employing contactors.
Heating Systems:
Electric furnaces and heating elements are two more heating applications that use contactors. They guarantee the dependable and secure functioning of these systems.
HVAC Systems:
Contactors regulate fans, compressors, and other parts of heating, ventilation, and air climate (HVAC) systems. Maintaining ideal interior conditions requires this application.
Importance of Contactors in Power and Automation
Safety:
In electrical systems, contactors offer a crucial safety feature. By stopping the current flow, they aid in preventing overloads and short circuits, safeguarding both workers and equipment.
Efficiency:
Contactors improve operational efficiency by enabling the automation of power control. They make it possible to precisely control lighting and machines, which lowers energy usage.
Reliability:
Reliable functioning in challenging conditions is ensured by high-quality contactors. They are appropriate for ongoing usage in industrial settings due to their sturdy design and longevity.
Versatility:
Applications for contactors are numerous and span from basic lighting control to intricate automation systems. They are a preferred option for electrical engineers and technicians due to their versatility.
Selecting the Right Contactor
Take into account the following elements when selecting a contactor for your application:
Load Type:
The choice of contactor may be influenced by the distinct properties of various loads, such as capacitive, resistive, or inductive. Choosing the appropriate contactor requires an understanding of the load type.
Current and Voltage Ratings:
For your application, make sure the contactor can manage the necessary voltage and current levels. Contactors that are overrated or undervalued may fail or be ineffective.
Coil Voltage:
The coil voltage of the contactor you choose should match the control circuit. Selecting a coil voltage that meets the requirements of your system is crucial because they can differ.
Environmental Conditions:
Take into account the operating environment of the contactor. While some contactors are made to withstand harsh environments, some are better suited for indoor use.
We at Rudra Power & Automation understand how important contactors are to contemporary electrical systems. You may improve safety, dependability, and efficiency in your operations by making well-informed decisions by being aware of their types, functions, and applications. Selecting the appropriate contactor is essential for optimum performance, regardless of whether you are wanting to create a new system or modify your current ones.
Please get in touch with us if you need help choosing the right contact for your particular requirements or if you have any questions. In order to help you identify the best solutions for your applications, our team of professionals is available to assist you in navigating the intricacies of automation and power.
