Solid State Relays (SSRs)

A Complete Guide on Solid State Relays (SSRs)
Introduction to Solid State Relays (SSRs)
Electronic switching devices known as solid-state relays (SSRs) regulate power circuits without the need for moving parts. SSRs use semiconductor devices to do the same task as traditional electromechanical relays, which use mechanical contacts to open and close circuits. SSRs are a popular option in many applications, ranging from consumer electronics to industrial automation, thanks to this technology’s many benefits.
How Solid State Relays Work
Transistors, diodes, and thyristors are examples of semiconductor components used in solid state relay operation. The semiconductor is activated and current can flow through the output circuit when a tiny control voltage is applied to the SSR’s input side. Because this procedure is immediate, switching times are faster than with electromechanical relays.
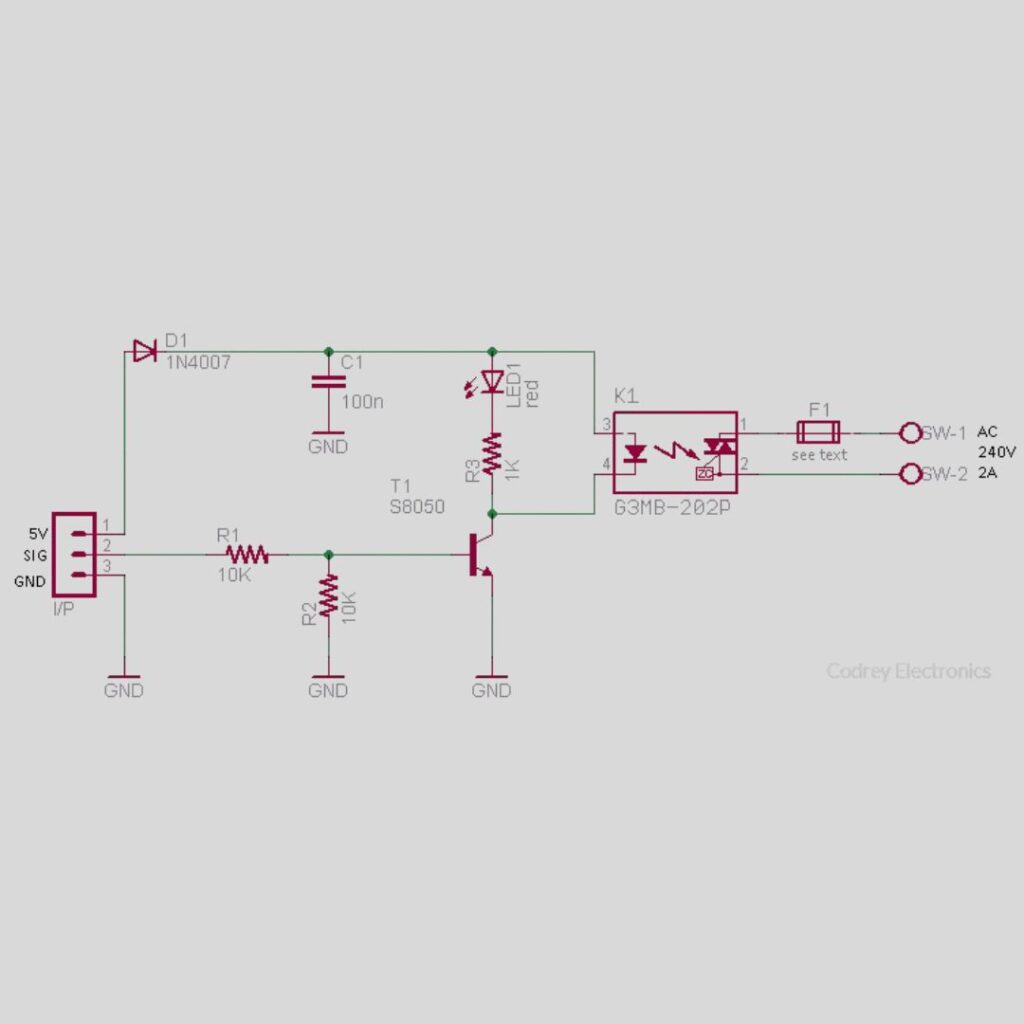
Key Components of SSRs
Input Circuit:
Here’s where the signal for control is applied. Signals with low voltage DC or AC can trigger it.
Opto-Isolator:
By establishing electrical isolation between the input and output, this part makes sure that high voltages cannot harm the control circuit.
Output Circuit:
Depending on the requirements of the relay, this component connects to the load and is capable of handling high voltage and current levels.
Heat Sink:
In order to ensure dependable functioning, many SSRs need a heat sink to disperse heat produced during operation.
Solid State Relays (SSRs) Brand
- Carlo Gavazzi
- Crydom
- Fotek
- Omron
- Panasonic
- Schneider
- Siemens
Advantages of Solid State Relays (SSRs)
Solid state relays are superior than conventional electromechanical relays in a number of ways:
- Quicker Rates of Switching: SSRs are perfect for applications demanding quick reaction times since they can turn on and off in microseconds. In automated systems where timing is critical, this speed is vital.
- Extended Life Expectancy: Because they do not have any wearable mechanical parts, SSRs have a far longer operational lifespan. They are appropriate for continuous usage in difficult environments since they can withstand millions of switching cycles.
- Silent Operation: Because they do not have any moving parts, SSRs run quietly. This feature is especially helpful in situations where noise reduction is essential, like in homes or workplaces.
- Compact Size: SSRs are often smaller than their electromechanical equivalents; control panels and other equipment can make better use of available space.
- High Reliability: SSRs are less likely to fail as a result of vibration, shock, or environmental factors because they do not have mechanical connections. In industrial applications where downtime can be expensive, this reliability is crucial.
- Electrical Isolation: SSRs’ opto-isolators offer superior electrical isolation between the load and control circuits, boosting security and shielding delicate parts from spikes and high voltages.
Applications of Solid State Relays
Applications for Solid State Relays are numerous and span numerous sectors. Here are a few typical applications:
Industrial Automation:
Solid State Relays are widely employed in industrial settings to regulate heaters, motors, and other large machinery. They are perfect for procedures that need precise control and dependability because of their durability and quick switching capabilities.
Temperature Control Systems:
Solid State Relays are frequently used in HVAC systems, furnaces, and ovens, among other temperature control applications. By quickly turning heating elements on and off, they can precisely control temperature, guaranteeing peak performance and energy economy.
Lighting Control:
Solid State Relays can be used to operate dimmers, LED lights, and other lighting fixtures in both home and business lighting systems. They are appropriate for contemporary lighting solutions due to their small size and quiet operation.
Medical Equipment:
Solid State Relays are utilised in a variety of medical devices, such as surgical instruments and diagnostic equipment. Their dependability and safety characteristics are essential for guaranteeing that life-saving equipment operates as intended.
Consumer Electronics:
Solid State Relays are used in many consumer electronics products for effective power control, including coffee makers and washing machines. These applications are perfect for them because of their capacity to manage large currents without sacrificing compact form factor.
Choosing the Right Solid State Relays (SSRs)
When selecting a Solid State Relay for your application, consider the following factors:
Load Requirements:
Find out the load’s voltage and current requirements that you want to manage. Make that the SSR is capable of meeting these demands without going beyond its rated capacity.
Control Signal Type:
Make sure the Solid State Relay is compatible with the control signal type (DC or AC) that you intend to use. While some SSRs can handle both AC and DC loads, some are exclusively built for AC loads.
Switching Speed:
Think about the switching speed your application needs. If quick switching is necessary, go for an Solid State Relay with quick reaction times.
Heat Dissipation Needs:
Based on the load and operating circumstances, determine if the S Solid State Relay needs a heat sink. Relay lifetime and dependability depend heavily on proper heat management.
Environmental Conditions:
Examine the surroundings in which the Solid State Relay will function. Variations in temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals or dust can affect how well the relay functions.
Installation and Maintenance of Solid State Relays
Proper installation and maintenance are vital for ensuring the optimal performance of Solid State Relays:
Installation Tips:
- Observe Manufacturer Instructions: To guarantee correct setup and operation of the Solid State Relay (SSR), always go by the manufacturer’s installation instructions.
- Utilise appropriate wire: Make sure the load and control signals are compatible with the wire being used. For dependable connections and to avoid overheating, use the appropriate gauge and kind of wire.
- Mounting Considerations: Place the SSR where sufficient ventilation and heat dissipation are possible. Keep it out of enclosed areas with no ventilation.
- Installation of the Heat Sink: To efficiently manage heat, if necessary, mount a heat sink to the SSR. To improve heat transfer between the SSR and the heat sink, make sure the thermal paste is applied correctly.
Maintenance Tips:
- Frequent Inspections: Look for indications of wear, damage, or overheating on a regular basis in the SSR. Examine any discolouration, burnt connections, or strange odours.
- Clean Environment: Make sure there is no dust or other debris in the vicinity of the SSR that could interfere with its operation.
- Monitor Performance: To identify any possible problems early, keep a watch on the SSR’s operational metrics, such as switching times and load performance.
- Replace as Necessary: To prevent more systemic issues, replace the SSR as soon as it begins to exhibit symptoms of failure or performs below expectations.
Solid State Relays offer numerous advantages in terms of reliability, efficiency, and safety across various applications. By understanding their features, selecting the right SSR for your needs, and following proper installation and maintenance practices, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity in your systems. Whether in industrial automation, temperature control, lighting, medical equipment, or consumer electronics, SSRs play a crucial role in modern electrical control systems.
